In this tutorial , i will show how to create melody using microcontroller and in this tutorial i will use pic18f2550 microcontroller .So let's create a project in proteus .
Proteus Project :
Please follow the instructions given below :
Now pick pic18f2550, sounder, crystal,22pf capacitor,VDD and ground according to the instructions given below :
Now complete the circuit as given below :
MikroC Code :
Source Code :
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void Tone1() {
Sound_Play(659, 250); // Frequency = 659Hz, duration = 250ms
}
void Tone2() {
Sound_Play(698, 250); // Frequency = 698Hz, duration = 250ms
}
void Tone3() {
Sound_Play(784, 250); // Frequency = 784Hz, duration = 250ms
}
void Melody() { // Plays the melody "Yellow house"
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3();
Tone3(); Tone3(); Tone2(); Tone2(); Tone1();
}
void ToneA() {
Sound_Play( 880, 50);
}
void ToneC() {
Sound_Play(1046, 50);
}
void ToneE() {
Sound_Play(1318, 50);
}
void main() {
ADCON1=0x0F; //disable adc
CMCON=7; //disable comparator
Sound_Init(&PORTC,0);
Sound_Play(880, 1000); // Play sound at 880Hz for 1 second
while (1) {
ToneA();
delay_ms(100);
ToneC();
delay_ms(100);
ToneE();
delay_ms(100);
Melody();
}
}
Sound_Play(659, 250); // Frequency = 659Hz, duration = 250ms
}
void Tone2() {
Sound_Play(698, 250); // Frequency = 698Hz, duration = 250ms
}
void Tone3() {
Sound_Play(784, 250); // Frequency = 784Hz, duration = 250ms
}
void Melody() { // Plays the melody "Yellow house"
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3(); Tone3();
Tone1(); Tone2(); Tone3();
Tone3(); Tone3(); Tone2(); Tone2(); Tone1();
}
void ToneA() {
Sound_Play( 880, 50);
}
void ToneC() {
Sound_Play(1046, 50);
}
void ToneE() {
Sound_Play(1318, 50);
}
void main() {
ADCON1=0x0F; //disable adc
CMCON=7; //disable comparator
Sound_Init(&PORTC,0);
Sound_Play(880, 1000); // Play sound at 880Hz for 1 second
while (1) {
ToneA();
delay_ms(100);
ToneC();
delay_ms(100);
ToneE();
delay_ms(100);
Melody();
}
}
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
Now follow the next instructions .



















 .
.

![Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step] Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiZ5-tClK21bTzzAENS5_3z5AjaxDWaUaLxwq7P5gy_MWhpdSGXrd1XpbsQLGK5KXTrpEyVIz9KVCMjxjv48K_pA_uXtZORHzRGgxvTiPxjo9hpVkdB0ULptbzxMLuhiZ3TF1im3rz3k3Q/s320/Untitled.jpg)
![Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step] Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgq3KnHwv1zCLTxtVO49UJLtLFzmRClhgrI1rp-so3uCVDtkm5iriBv4qrDz7wftDAZHVdha6UQJbAauq8e4rbtz1_YJAhmNTsEuJ5jABtu6BLd1HnJxYkK4wLyqWARlVNzqZbYiK6o_WZi/s1600/pic_2.jpg)

![Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step] Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiZ5-tClK21bTzzAENS5_3z5AjaxDWaUaLxwq7P5gy_MWhpdSGXrd1XpbsQLGK5KXTrpEyVIz9KVCMjxjv48K_pA_uXtZORHzRGgxvTiPxjo9hpVkdB0ULptbzxMLuhiZ3TF1im3rz3k3Q/s400/Untitled.jpg)
![Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step] Matrix [4x4] Keypad interfacing with PIC Microcontroller [ PIC18f2550 ] in Proteus [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj0jhV_Wi0MzKIOfw4E4Nm9I1cjwbzUS0u7HUilhLgrndKYAKrFUeJyLKkSzm-tYnLr13PRXLBYUraCynlKKXt5bgw0FzuBDQ6qSTPSEEHrYdhPLvFki7PykUvNWUzJPvX9q4ywanXnmU2X/s1600/runproteus.jpg)

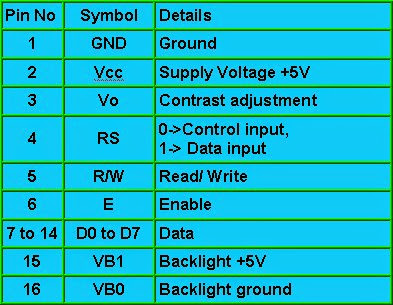

![Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step] Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhDui957yda-dVg_N-GUvgm5qOe3DmAklAIX7xoJXFYeGxn4iDNDg1N68bWn_jY5GSsIGbROxP2yFXC93TNgrVY6calhXr9JNiFD176dtTX4o06hST95oZ2Ait2vd6OaqXx_QKWV4ZYNcA_/s1600/lcdinterface.jpg)
![Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step] Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjTpes4X3zY2O2-g3ESYa-1d6rWyL8FCQQ2rQSCRd8xBDxUsPMU9AuPLpDypF8Fk1CSJZToDP6112bKC4iWX2JYK53eYA7g1Lo0TorZGe6ft6m3fsWs6phboAwmnCKwRr3Z9mrX3YPv1q8x/s1600/lcdtutorial.jpg)
![Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step] Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiMlpnrtTPEfOTnOEpnzUIki0h68fYzyQugW19JhEb7sBigj8YCEW2-B_HM7TOlewTh7aXdXVqOccVABWRiQOjoSkjgt_5t7xXKQm70thxbjUTSJcpal2flMXAxSmHo9m8MuVDkDQm7MV6-/s1600/scroll_1.jpg)
![Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step] Lcd 16x2 Scrolling Display Using PIC Microcontroller [Step by Step]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiiPNrpsvwehIWS3vGTlGYbgKACkIqbDQ3nL-U_Gee51sB23ERlJ5z3_EEu8uIjSPVdJ30ha3yQz7eG_afC1ksfCsj-SsjMombiYfVjh6Mwp-es4-5nC1HpW92HAdxBUclhvY_smu-a1DyG/s1600/scroll_2.jpg)
















